How do you decide if the risk of a security feature is worth it? If the cure can be as bad as the illness how do you decide? We have opinions!
Cisco owes me a sandwich!
In 2010 we were so excited to meet with a team at Cisco to discuss our network function virtualization offering that had been live in the clouds since 2008.
The folks at Futuriom (@rayno, aka R. Scott Raynovich) have put up a nice piece about Cisco’s struggles to integrate its many acquisitions and fundamentally retain relevance. Now of course Cisco is a behemoth compared to Cohesive Networks, we are a lean and cute marsupial next to it the hulking mammal, but we do compete with them all the time and they do represent the other side of about 50% of all our customer’s connections. (My point being we are quite familiar.)
So, way back when cloud was young – our parent company CohesiveFT developed a very strong champion at Cisco.
He loved what we did with the VNS3 platform (then the VPN-cubed appliance) and was both fascinated and skeptical that via an API you could create any over-the-top network and route traffic through it, indifferent to the actual underlying networks. You could have a flat network anywhere with dynamic routing protocols in place, a form of server motion which separated network location from network identity, thus enabling very flexible and secure application systems. In many ways, unbeknownst even to ourselves, in 2008 we had created the first commercial cloud native NFV (network function virtualization) solution with a restful API.
We ended up invited to Cisco campus in California for what would be a pretty significant (for us) meet up with some of their key technical and business development decision makers about our virtual appliances. We were thrilled and hoped for a partnership to accelerate our business.
The calendar snippet above shows that it was a morning meeting – and maybe I have conflated events through time, as in my memory it was thereafter rescheduled into a longer, later lunch meeting (catering provided) with time for a demo and hopefully some whiteboarding with the team.
The meeting was well attended by our champion, key technical people and decision makers.
We launched into our pitch about how you could build networks anywhere you had access to compute and bulk network ingress/egress. Some questions came and went – and we were thrilled to be talking about the flexibility and security that comes with network virtualization.
At about 20 minutes in, product managers were scribbling away in their notebooks, but then the “biggest” of the technical folks looked up and said “Wait, wait, this is a hardware appliance, right?”
“No, no,” we say, “it’s virtual; all software, really flexible.”
To which he said, “No one will ever put network traffic through software” and he closed his notebook, stood up, and began exiting the room.
With the exception of our champion, everyone else followed.
As we were leaving the room, there was the catering cart outside that had not yet had a chance to come in to our truncated meeting. My memory is sandwiches – but maybe it was breakfast items, regardless it was now NOT on offer, and we were exited from the building.
So, two takeaways, network virtualization was real, driven by software and took Cisco a long time to get their heads around, and I think Cisco owes me a sandwich (or perhaps a croissant).

Migrating to IPv6 – Managing the Madness (Pt. 1)
Names, Names, Names.
Its the year enterprises get focused on moving to Internet 6. We think it is mostly because of the AWS IPv4 address price increase, but as good a reason as any.

While we don’t expect you to start using ALL of the eighteen quintillion, four hundred forty-six quadrillion, seven hundred forty-four trillion, seventy-three billion, seven hundred nine million, five hundred thousand addresses in your cloud VPCs and VNETs, do remember nature abhors a vaccuum.
If you combine the enormity of the address spaces, and the somewhat impossible-to-verbalize representation of addresses, using addresses as a point of reference at the surface of network administration, monitoring, or security is not going to work much longer.
It is time to let loose your “wordsmiths”!

All of those devices running around your organization need a name, and in fact once we start naming things it won’t stop, we will have multiple names per device, because if one name is good, more are even better.
Of course organizations have been using DNS for years, and the Internet runs on it, but for B2B, enterprise, SaaS we have seen widely varying depths of use.
Some of our more advanced customers have adopted one or more taxonomies for naming devices in their production SaaS environments, albeit perhaps not throughout their internal organization. It can be somewhat of the cobbler’s children having no shoes, we do pay attention to our customers, but often not to ourselves. Here is an anonymized example of such a SaaS taxonomy:
<saas service name abbreviation>.<cloud>.<cloud account abbreviation>.<cloud region>.<production status flag>.<customer id>.<customer abbreviation>.<cost center id>.<machine id>.<cloud instance id>.domain
It is certainly a mouthful, and in fact more so than “fc55:636f:6865:7369:7665::6440:1fe3”, but since most humans DON’T do hex/decimal calculations in their heads, it works by providing understanding via the delineated labels in the full name.
Once you see this type of naming at work in administration and monitoring, you can then see why devices end up with multiple DNS names based on differing organizational taxonomies. We have see technical, organizational, asset management, project-based, and functional naming schemes for devices. At Cohesive we aren’t quite that complex, but if you ask Chatgippety or the LLM of your choice for examples they will provide some overly simplistic examples which give you the gist.
- dell.laptop.8gb.intel.corei5.lenovo.windows.10.ssd.departmentC.corporate.com
- marketing.sales.promotions.abrown.laptop.hr.central.branch.corp.com
- asset.laptop.s345678.la.abrown.decommissioned.finance.southern.us.corp.com
- project.gamma.phase3.teamC.abrown.task3.testing.chicago.corp.com
- function.sales.system.crm.module3.midwest.corp.com
Further Reading
If you have all of naming nailed, good on you. If you don’t here is a great overview by the folks at Cloudflare who create some great content for all of us: https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/dns/what-is-dns/.
For those who are more visual, here is excellent work from a redditor who seemed to have become inactive (sadly) three years back:
https://www.reddit.com/r/programming/comments/klaffg/dns_explained_visually_in_10_minutes/.
For more on the emerging challenges of the IPv6 world you can look back at a few Cohesive posts:
- https://cohesive.net/blog/moving-to-ipv6-herein-lies-madness-part-1/
- https://cohesive.net/blog/moving-to-ipv6-herein-lies-madness-part-2/
And if IPv6 addressing still has you perplexed the team at Oracle did a super job here:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E18752_01/html/816-4554/ipv6-overview-10.html.
AND – never forget the Rosetta Stone of IPv4 to IPv6 understanding here:
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1pIth3KJH1RbQFJvZmZmpBGq6rMMBhqEmfK-ouSNszNY.
Next up we will show you how VNS3 version 6.6 for Internet6 will help you adopt IPv6 for cloud edge and cloud interior, provding network functions that are better, faster, cheaper than the competing offerings (to NAME just a few reasons to get a Cohesive network).
Moving to IPv6 – herein lies madness (Part 2)
This post is short and essential.
The are two Internets now: the IPv4 Internet and the IPv6 Internet.
The IPv6 Internet is not related to the IPv4 Internet as you have configured it inside, outside, or at the edge of your Enterprise.
IPv6 is not the next version of the Internet protocol; it is the next Internet.
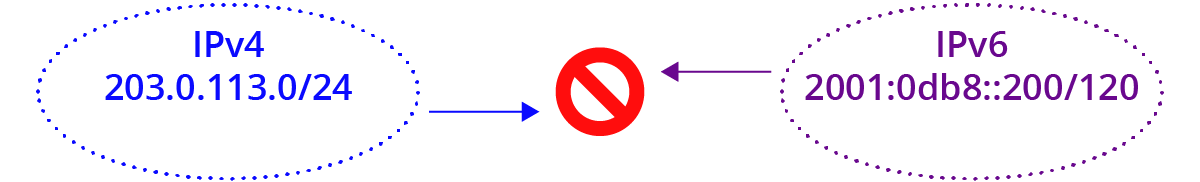
This is the best way to think about it in order to have a more intuitive feel of what is happening underneath it all.
AND – the two Internets never meet. Meaning they are side by side, and applications can move data between them, but in their essence they are different Internets.
Both Internets move across the same layer 2 and physical links, and the protocols above them largely work the same on both, but they are distinct at layer 3, where addressing and naming and routing and firewalling and flow control and many other Internet-y things happen.
A computer may exist on either or both Internets concurrently; an application may bind a network socket to either or both; but they are entirely separate and unrelated.
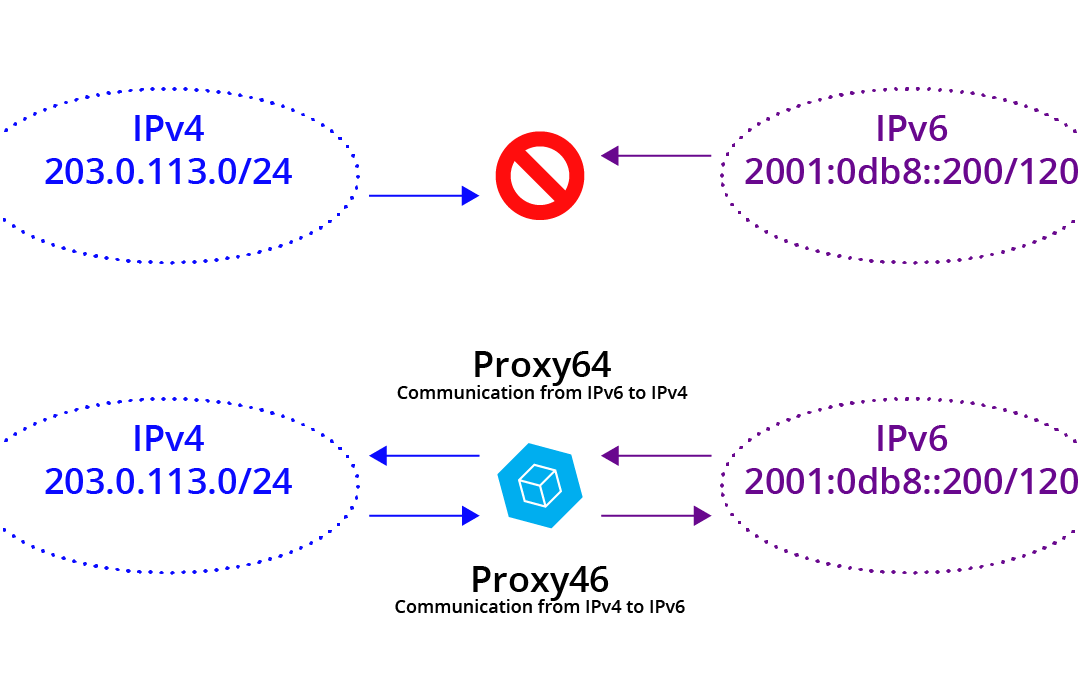
You will hear about NAT64 (and some NAT46) and the implicit description that addresses are being translated from 6-to-4. I am sure that is the name that will “win” in the industry, but this is a place where we will stand apart. We are calling it Proxy64 and Proxy46, as that is a more realistic and familiar description of what is actually happening. It is not address “translation” in the long standing sense, it is packet TRANSMOGRIFICATION* (according to rules which are in some ways “NAT-like.”) It pulls the payload out of an IPv6 packet and creates an entirely new IPv4 packet. (Some concepts don’t even translate well between the two; these cases are handled by different sofware anywhere from “poorly” to “confusingly.”)
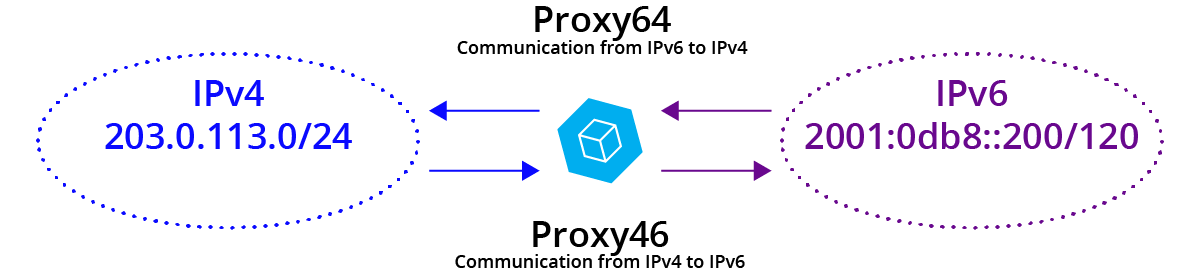
Cohesive’s VNS3 6.6.x is moving out into customer’s hands and with it, our Proxy64 and Proxy46 plugins for communicating between the two Internets.
Let us know how we can help your teams get connections up and running at cloud edge using IPv6.
(ps. If you are just coming up to speed on IPv6 here is a good primer from Microsoft. The “producer-centric” nature of IPv6 comes through, but is a good summary of the industry description and belief systems (don’t let the ‘dotnet’ in the URL scare you).
*Yes that is a C&H reference
Moving to IPv6 – herein lies madness (Part 1)
Well, it’s finally happened. It’s the “year of IPv6” for the enterprise.
With this transition will come a significant amount of “cognitive load” for enterprise application and infrastructure administrators.
After a decade or more, it appears there will finally be a broad-based move to Internet Protocol version 6. All it took was for Amazon to announce a price increase for the use of IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) addresses.
IPv6 has been being deployed incrementally since 2012 – but for many of us it has been via background adoption by consumer products that we may not even been aware of; cable companies and mobile phone vendors providing the infrastructure to our homes and devices.
For the b2b software and infrastructure technology used by the enterprise, it remains new and novel. For example, Amazon Cloud has supported some IPv6 for a number of years, both dual stack and single stack, whilst Microsoft Azure Cloud only began in earnest in 2023. Both platforms still have significant limitations and fragmentation of support across products.

So if the tech titans are just getting their heads around IPv6, what are us “normies” supposed to do?
At Cohesive Networks, our plan was to start slipping in support over the course of this year, finishing sometime in 2025 for an expected enterprise demand in 2026. Why haven’t we supported to date? Frankly, “no one uses it” – in that of the SaaS, PaaS, and BPaaS companies we support, none of them have asked for it……until the AWS price increase. Our metal-based competitors like Cisco and Palo Alto have supported it for years, but from our broad experience working with our customers, and our customer’s customers, and our customer’s customer’s outsourced network support people, the feature was a tree falling in the forest.
While there is a need to expand the available address pool, there is conflict and confusion between the “producer-centric” intelligence that created IPv6 and its revisions and implementations to date, and the practical needs, the “consumer-centric” needs, of the people just trying to get their jobs done.
There is a disconnect between the simple needs that we satisfy with IPv4; deploy a server, deploy 10 servers, deploy a cluster of a couple hundred servers; and the massive scale of IPv6 which immediately confronts its business consumers.
At Cohesive, we have done a decent job of reducing much of networking and security to “addresses, routes, and rules.” But even for us, helping customers deal with three hundred forty undecillion, two hundred eighty-two decillion, three hundred sixty-six nonillion, nine hundred twenty octillion, nine hundred thirty-seven septillion addresses is a challenge.
Ok, that number above is the whole space, so maybe I am being overly dramatic.
Let’s just get an AWS VPC or Azure VNET with a single IPv6 subnet; that should be easier to deal with.
Minimal size is a /64, that sounds better. Oops, that is 18,446,744,073,709,500,000 addresses! (For those of you speaking it aloud, that’s eighteen quintillion, four hundred forty-six quadrillion, seven hundred forty-four trillion, seventy-three billion, seven hundred nine million, five hundred thousand addresses).
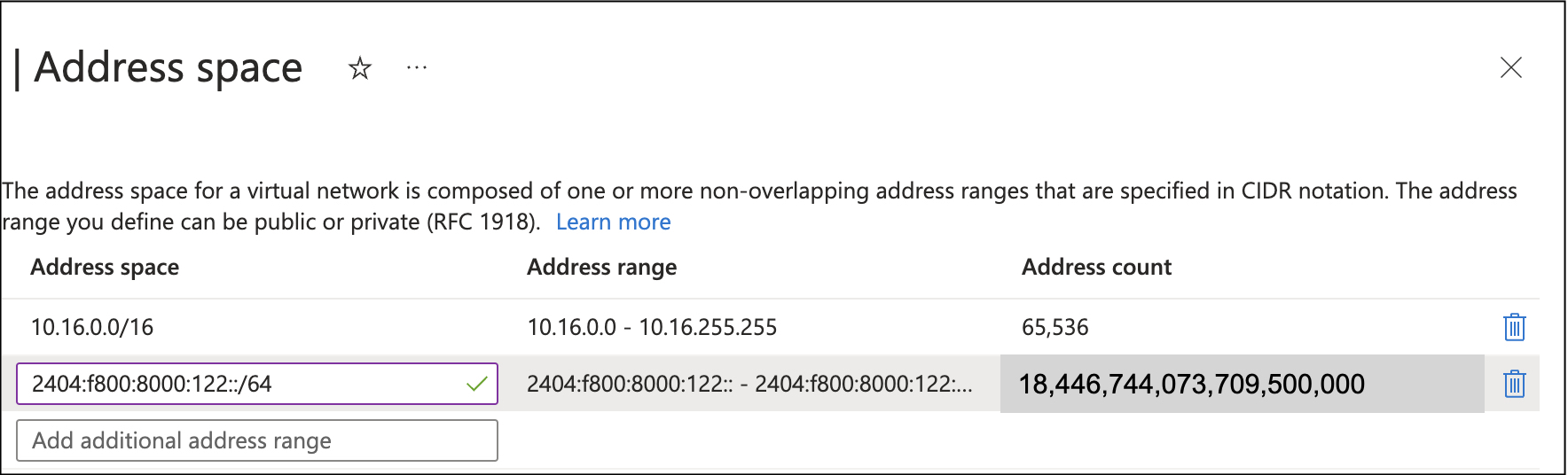
And for every virtual network/subnet – another eighteen quintillion.
Now, if I have 10, 100 or 1000 servers to deploy – what does it matter? Just use some addresses and carry on.
True enough, but the fact that they come from a potential space of 1.8 x 10^19 is serious cognitive load that is presented to the infrastructure operators, and it is naive to think this doesn’t come at a cost. As computer memory went from 512k on a “FAT MAC” to 96G on my MacbookPro, I didn’t have to confront the gap between 524,288 bytes and 103,079,215,104 bytes in the normal course of my work.
So what do we do? Well for our part, as we release VNS3 6.6 (with IPv6), we are reducing some of this cognitive load and will be working with our customers to ever-simplify the move to IPv6.
In the meantime, here is a Google Spreadsheet we created for our internal use to help us get our heads around the magnitude of the IPv6 space. Feel free to share: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1pIth3KJH1RbQFJvZmZmpBGq6rMMBhqEmfK-ouSNszNY/edit#gid=0
Stand Apart – but be Cohesive
I received a number of congratulations on the LinkedIn platform last month when apparently it let people know I have been with Cohesive Networks for 9 years.
As I reflected on this one thing stands out in relief, and that is Cohesive has always “stood apart” within the markets it serves.
Cohesive Networks exists at the confluence of virtualization, cloud, networking and security. We are of course a part of this commercial market but have not been re-directed by every twist and turn of these markets that have come and gone. Flavor and fashion are often the order of the day, and no doubt we have adopted some of the descriptive labels through time. But the labels have not swayed us from our essential mission, getting customers to, through and across the clouds safely.
If you look at the Gartner hype cycle for cloud networking it provides a gallery of differentiators through time: network observability, container/kubernetes networking, multicloud networking, SASE, SSE, Network-as-a-Service, SD-branch, network automation, network function virtualization, software defined networking, zero trust networks, software-defined WAN, micro-segmentation. If you look at these different facets, the tools, techniques, and knowledge to implement these are not that different. What is different is the packaging and the go-to-market.
Because we have been providing a virtual network platform since the clouds began, we have had customers use us for all of these functions. As a result the good news is we have been less “swayed” by flavor and fashion, which has done well for our existing customer. The bad news is we haven’t always best communicated our value to the potential new customer who may be thinking very much in the context of one of these re-packaged approaches.
Our usual inbound leads are “Hi, I think we need your stuff” or “Hi, we are using a lot of your stuff, can we discuss volume discounts and support plans”.
This communication posture stems from the fact that we have often been ahead of our competitors in either implementation or insight, or both. We were the first virtual network appliance in the EC2 cloud, IBM Cloud, many of the “clouds no-more”, and at later dates among the first network and security appliances in Azure and Google.

Cohesive’s patents are for “user controlled networking in 3rd party computing environments”. It is a subtle distinction – but powerful, between what an infrasturcture administrator, network administrator or hypervisor administrator could do at that time, and the freedom of our users on that infrastructure to create any network they wanted. These are encrypted, virtual networks that their infrastructure providers know nothing about, can not see, nor control. Our users in 2009 and beyond could create any secure, mesh, over-the-top network they wanted without the need or expense of the network incumbents who came before us. These customers find us significantly easier, significantly less expensive and made for the cloud without “metal” roots dragging them back to the ground.
When we showed this capability to investors, partners, infra providers, acquirerers – many of them said “I don’t get it” or “we’ll do better (someday)” or “you have to do all this in hardware” and more. By comparison, the customers who found us through web search, cloud conferences, and cloud marketplaces said “that’s what I need” and a subscription cloud networking company was born.

Looking back, it is shocking that our first offering was “virtual subnets”. It is amazing to think about it, but we sold subnets! At that time any cloud you used put your virtual instances in a very poorly segmented 10.0.0.0/8 subnet of the compute virtualization environment. People wanted to control addresses, routes, and rules, and our encrypted mesh overlay provided it. That was our first product-market fit, and of course that has evolved considerably.
This set us on the path of listening to our customers, and asking ourselves quite fundamentally what a network is, and what is it used for, and by whom?
So while we stood apart, of course we were Cohesive.
Networks are all about standards and interoperability, we just did it our own way.
The feedback from customers was “yes” and “more please”. The feedback from the experts often remained “huh”. So we pressed forward in our own autonomic and somewhat autistic manner, only listening to certain market signals and obsessively working to fulfill a vision of networking and security that says “networks are addresses, routes and rules, everything else is implementation detail the customers should rarely see.”

Now in 2024 and beyond, as the chaotic streams of the changing cloud markets, Internet Protocol v6, and the needs for secure AI and private AI collide, my guess is we will still stand apart while still being Cohesive.
Enterprise WireGuard® with Cohesive VPN Client

VNS3 6.0 Beta3 will be available in cloud marketplaces or upon request this week (contactme@www.cohesive.net). In our last post we showed how easy it is to connect your native WireGuard® clients to VNS3 6.0. In this post we show you how to use the Cohesive VPN Client to achieve the same goals like connecting to data centers or cloud VPCs/VNETs, and managing your own WireGuard® network connecting multiple people and devices. In addition, we will show an overview of using our enterprise capabilities like dynamic route updates, easy tunneling of all traffic with local subnet exceptions, and OIDC integration so you can authenticate your vpn users with Google Authentication, Okta, Auth0 and more.
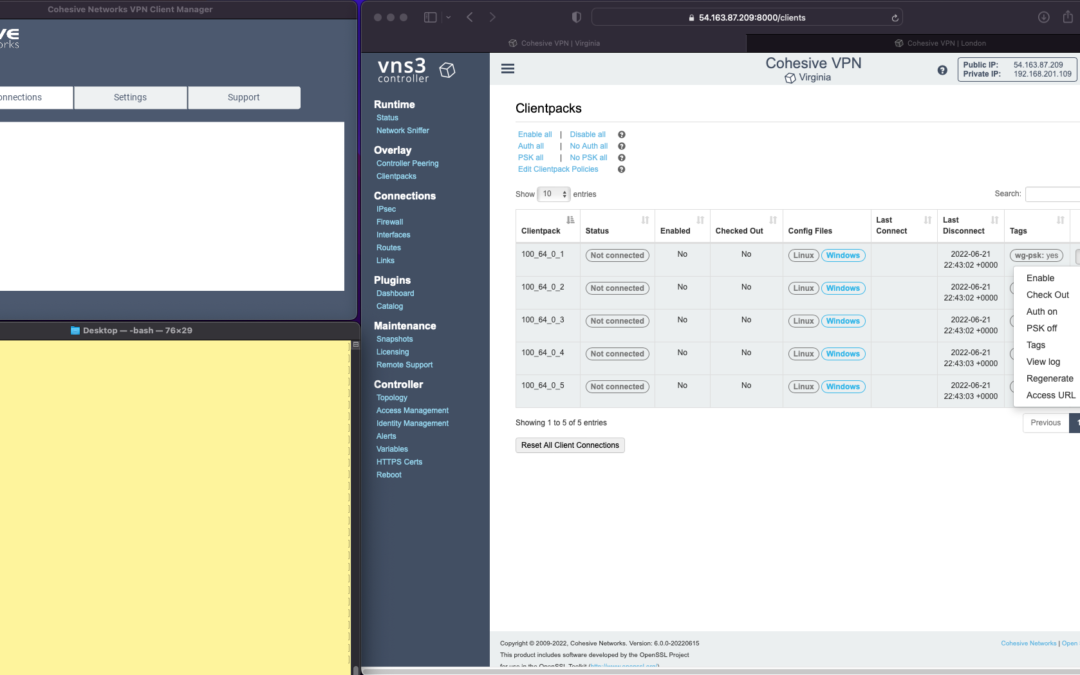
The screen shots throughout show three windows; upper left the Cohesive VPN client, bottom left a command line from the same Mac, and to the right the cloud-based VNS3 server.
VNS3 Network Platform has the concept of “clientpacks” – basically the credentials needed to connect a machine or a person to the network via a VPN client. Historically “clientpacks” have been “openvpn” by default. Starting in 6.0 clientpacks are WireGuard by default. In a future release we will support a dual stack with both “ovpn” and “wg” connections simultaneously, and a goal of IPsec clients as well.
In the picture above and those below we show the “Clientpacks” page. From this you can perform key administrative functions like disabling addresses, re-generating credentials, updating pre-shared keys, and getting access URLs for secure and easy distribution of VPN credentials.
Access URL


Above shows the results of choosing “Access URL” and displaying its result. This is a secure, one-time, timed URL allowing users to copy/paste the clientpack, download it for import, or use via a QR code on mobile devices.
It has all the necessary information to make a connection using the Cohesive VPN Client – with or without PSKs.
The commented lines are used by CNVPN CLI and GUI for additional enterprise support; failover, dynamic route updates, and OIDC authentication.
Copy/paste the clientpack into the Cohesive client via the “Paste” option, and choose Save.
Connect


Next choose “Connect” from the Cohesive Client’s “Actions” menu – and the VPN connection is created. The VNS3 Clientpacks page then shows the status as “connected”.
Below shows access to the VPN network by successfully pinging the VNS3 controller’s VPN address. (By default, this connection can access other addresses on the VPN. If that’s not desired it is easily changed via the Firewall page.)


You can use the Action menu on the VNS3 Clientpacks page to perform administrative operations. For example, if you select “Disable” on the connection, the client is dropped from the VPN.
Similar operations can be performed to re-new or re-secure a connection by adding a PSK or re-generating keys (both of which require the clientpack to be redistributed to the user or device). As expected, when you enable a PSK for the connection, the user is unable to access the network. With the credential re-deployed with the appropriate clientpack containing the PSK, they are back on the net!
To see some of those operations in action, take a look at our previous post. Cohesive’s target is to provide organizations the ability to deploy their own enterprise VPN infrastructure. This could be managed by Cohesive via our SecurePass offering, or self-managed. Regardless, our initial focus for 6.0 is managed, enterprise WireGuard.
Dynamic Route Updates
One of our key enterprise features is dynamic route updates. For “people vpns” you can usually just tunnel all traffic through the VPN – making the VPN adapter the default gateway. However, for IoT and machine2machine vpns, dynamic routing is a critical capability. You allow the device to have its own local gateway but when routes arrive dynamically, the traffic begins to follow that path. If the route is removed from the network, the default gateway is used.
In the example below the configuration is changed to have “RoutePolling = True”, and on the VNS3 controller a route to 55.55.55.55 has been advertised through the VPN. In the terminal window route display there is not yet a specific route to that public IP.
Once re-connected, the route to 55.55.55.55 through the VPN is visible on the client as a result of the dynamic route updating.
If that route is disabled or removed from the VPN network, then it is removed from the client.


Tunnel All Traffic
Tunneling all traffic through the VPN to the Internet is a snap with the Cohesive VPN Client.
Set the client parameter “TunnelAllTraffic” to “True” AND make sure you have enabled firewall directives on the VNS3 Server to send all VPN traffic out to the Internet.
VNS3 Free edition comes with a default set of rules in a group called “VPN2Internet. Go to the Groups view on the Firewall page and enable these rules.
This will direct all traffic from your VPN client to the Internet, getting its address translated to the Public IP of the VNS3 controller.
What if you still want to be able to access local network resources like a printer or file server? In that case, use the “LocalRoutes” option to enter a comma delimited list of the network CIDRs you want to exempt from the VPN so they can be reached locally.
Now that all traffic is being tunneled, from the command line the public IP 8.8.8.8 can be successfully pinged. To “prove” this traffic is going into the VPN we show it via our Network Sniffer.


VPN User Authentication
So far the examples have just used WireGuard protocol with unique keys and pre-shared key (PSK) for the connections. What about more specific user authentication? For WireGuard in VNS3 6.0 we use OIDC (Open ID Connect), and will add LDAP support in future. (Our dual stack offering in future will allow simultaneous use of OpenVPN and WireGuard clients, with your choice of LDAP/AD or OIDC).
With OIDC support you create a VPN users and/or admins application in your OIDC provider and then configure VNS3 integration.

Once the OIDC configuration has been saved you can login. In this case we are using our Google Apps login. When “Connect” is chosen, a login screen pops up in the default browser.

Upon entering the correct password the login panel indicates success and the VPN client connects!

Next up we will show using the Cohesive CNVPN CLI on a Linux machine. For cloud overlay networks and over-the-top cloud networking, the CLI is a powerful way to bring your enterprise feature set to your cloud and multi-cloud deployments.
(“WireGuard” and the “WireGuard” logo are registered trademarks of Jason A. Donenfeld.)

Recent Comments